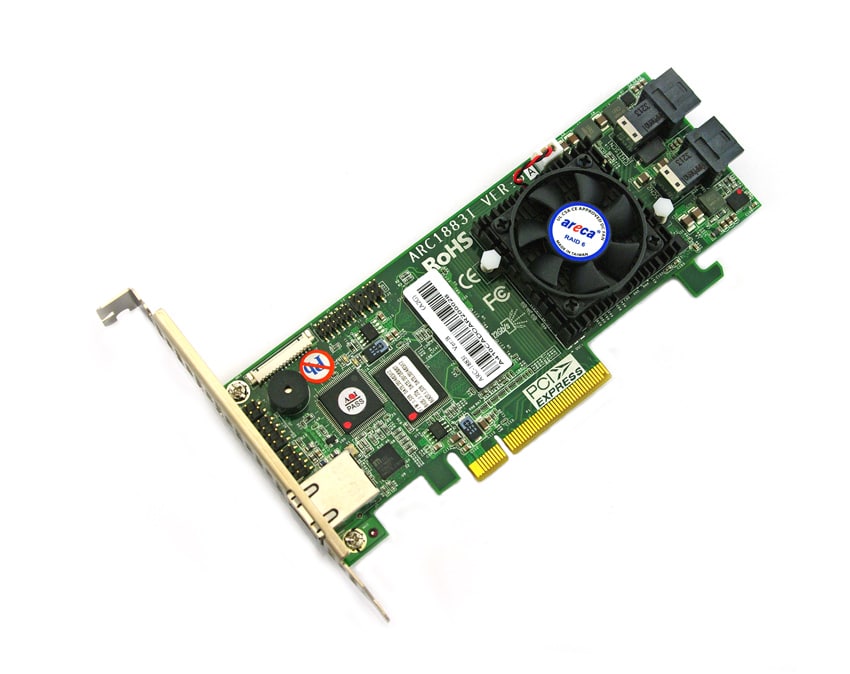
HighPoint high port count (HPC) NVMe RAID controllers are ideal for professional applications that require a small-footprint, mass-storage NVMe solution that can take full advantage of the PCIe 3.0 x16 transfer bandwidth. This performance-focused NVMe RAID architecture ensures that up to x4 lanes can be assigned to each device channel, and deliver up to 14,000 MB/s of transfer performance – ideal for professional media workstation and server environments designed to support a wide range of editing, rendering, capture and streaming applications.
HighPoint HPC U.2 NVMe Controllers allow customers to complete saturate the PCIe 3.0 bus-bandwidth with write performance over 14,000MB/s, while simultaneously supporting up to 120TB of storage capacity!
Open Disk Utility for me. In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose File RAID Assistant. Select a set type: Striped (RAID 0) set: A striped RAID set can speed up access to your data. You can’t create a RAID set on your startup disk; you must first start up your computer from another disk. Make Offer - HighPoint RocketRAID eSATA Controller for MAC Dual eSATA Port X4 RAID Controller High Point RocketRAID 642L 2 SATA 6Gb/s, Ports PCI-Express 2.0 x 4 SATA III $79.95.
The average write performance of a standard off-the-shelf U.2 NVMe SSD is approximately 2100MB/s.

Each high port count RAID controller features eight independent M.2 or U.2 channels, and can support from 16TB up to 120TB of storage capacity configured to act as independent drives or into one or more RAID 0, 1 or 10 arrays.
No other NVMe controllers in today’s marketplace can match the massive storage capability, blazing fast transfer rates or flexibility in such a compact package.

HighPoint high port count series NVMe RAID controllers are truly independent NVMe storage solutions. Unlike most NVMe devices in today’s marketplace, which are tied to a specific hardware platform or brand of SSD or motherboard, SSD7000 series controllers do not require a hardware environment with Bifurcation support, or any specialized software released by SSD manufacturers; any AMD or Intel motherboard with a dedicated PCIe 3.0 x16 slot can now support more than 120TB of NVMe storage, and experience sustained write performance in excess of 10GB/s via a single compact PCIe device.
Disk Utility User Guide
You can create a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) set to optimize storage performance and increase reliability in case of a disk failure. You can also create a set that concatenates smaller disks to act as one larger disk.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose File > RAID Assistant.
Select a set type:
Striped (RAID 0) set: A striped RAID set can speed up access to your data. You can’t create a RAID set on your startup disk; you must first start up your computer from another disk.
Mirrored (RAID 1) set: Protect your data against hardware failure with a mirrored RAID set. When you create a mirrored RAID set, your data is written to multiple disks so the information is stored redundantly. You can’t create a RAID set on your startup disk; you must first start up your computer from another disk.
Concatenated (JBOD) set: Increase storage space with a concatenated disk set. If you need one large disk, but you have several smaller disks, you can create a concatenated disk set to use as one large disk.
Select the checkboxes of the disks you want to include in the set.
For each disk, click the pop-up menu in the Role column and choose “RAID slice” or “Spare” to designate the disk as a standard member or spare in the set, then click Next.
Enter a name for the RAID set in the RAID Name field.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose a volume format that you want for all the disks in the set. (See File system formats available in Disk Utility.)
Click the “Chunk size” pop-up menu, then choose a disk chunk size that you want used for all the disks.
When you create a striped set, chunks of data from the same file are distributed across the drives. Ideally, you want data distributed across drives evenly and at an optimum size so that it can be efficiently accessed. If you want high data throughput from your set, choose a smaller chunk size so that data is spread across the drives and one drive can be accessing data while another is seeking the next chunk. With mirrored disk sets, choose a chunk size that matches the data you’re accessing. For example, when working with video files, your Mac is accessing large chunks of data, whereas when using a database of many small records, your disks may be accessing smaller chunks of information.
If you are creating a mirrored RAID set, select the “Automatically rebuild” checkbox to allow the set to be automatically rebuilt when member disks are reconnected.
Click Create.
Click Done.

If you have a Mac Pro with a Mac Pro RAID card, use RAID Utility. It uses the RAID card for better performance and to create more types of RAID sets.
Raid Controllers For Mac Pro 13.3

Raid Controllers For Mac Problems
Raid Controller For Mac Pro
